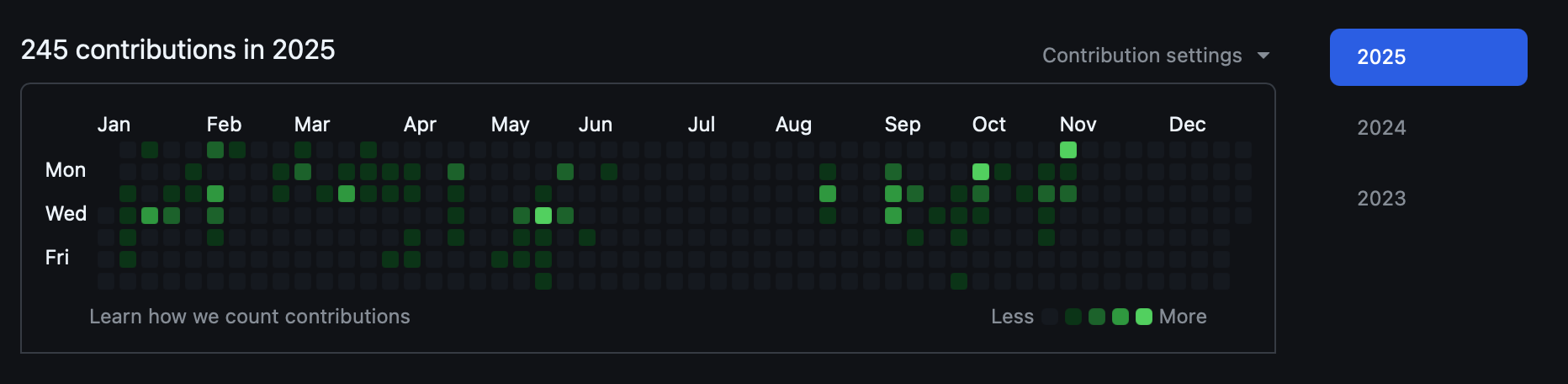
Start v.s. End
| Beginning of Year | End of Trimester 1 |
|---|---|
| Minimal Spring framework experience | Proficient in Flask & Spring backends |
| Basic coding skills with gaps in AP CSA topics | Strong AP exam readiness & technical skills |
| Struggled with project momentum and efficiency | Efficient collaboration & project completion |
Sidenote: Became a better speaker and able to communicate ideas and project more effectivley
Trimester Projects
Tools and Setup

Fundamentals of Javascript / Python
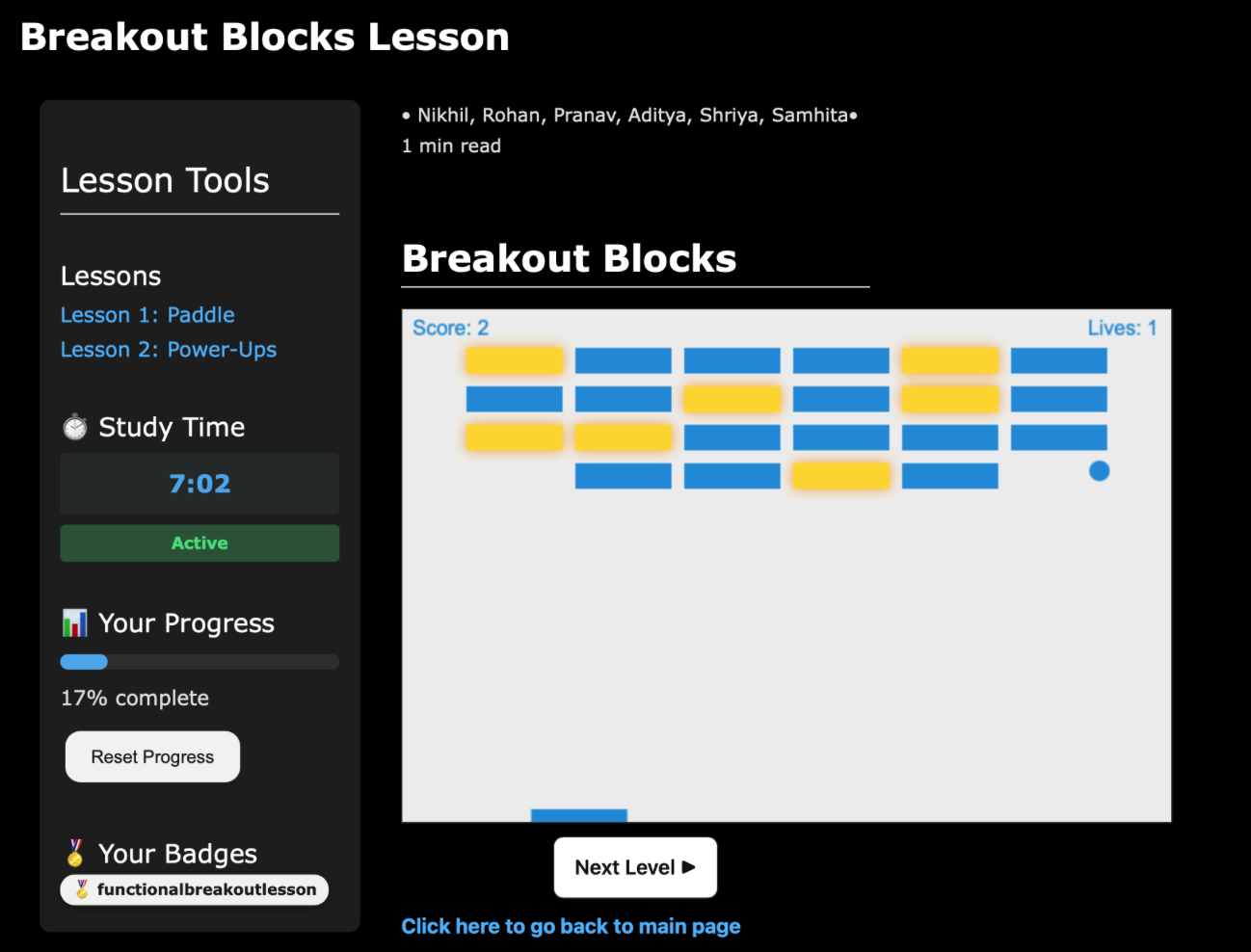
Profile/Linkedln Quest
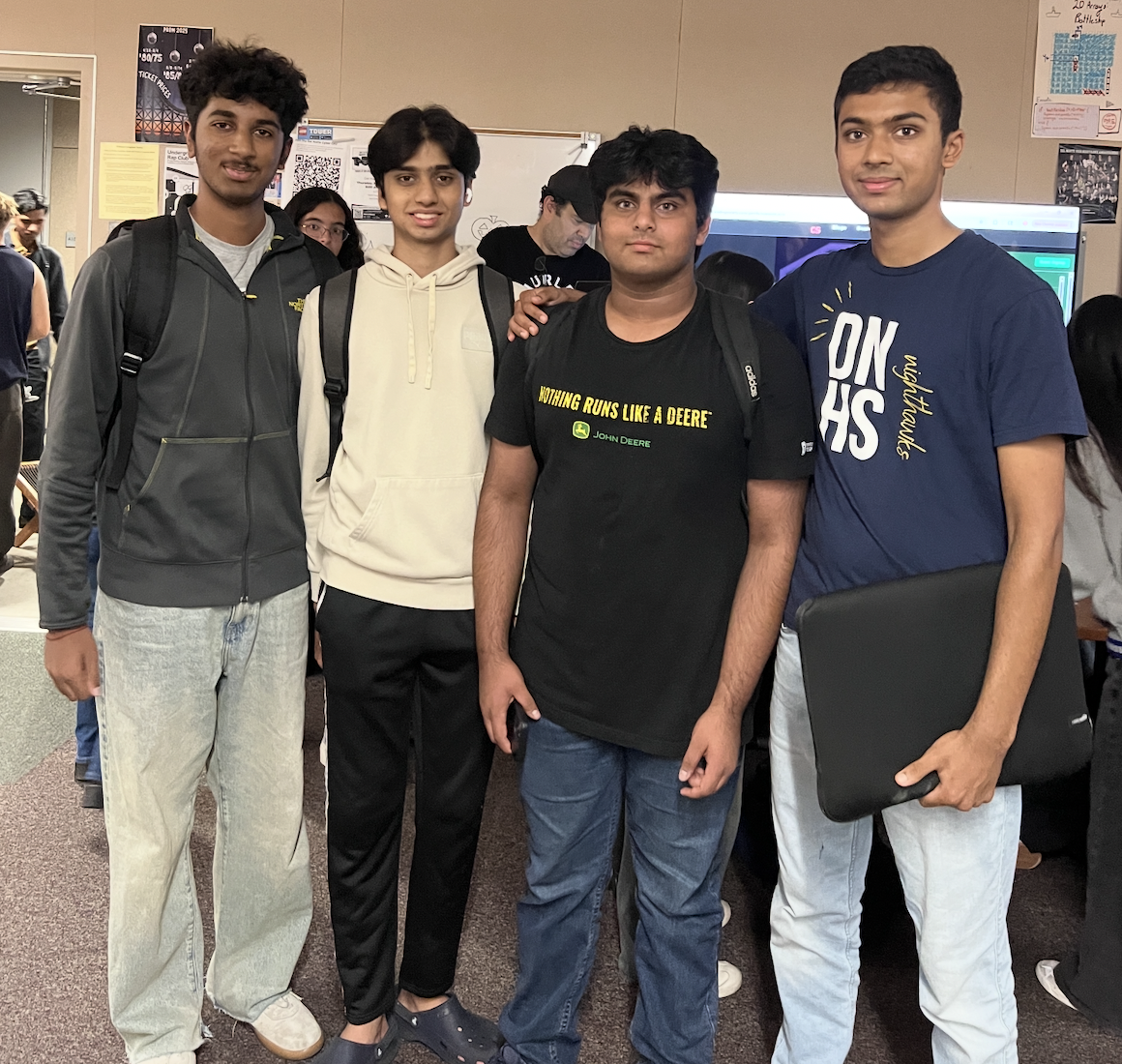
N@TM

Presentation
- Our Presentation:
- Delivered a well-coordinated presentation with diverse team members presenting different components
- Engaged attendees through personalized 1-on-1 explanations to parents and students, maximizing attention and understanding
- Successfully demonstrated all features without technical issues
- Effectively illustrated how the project integrates with the broader quest system for grading and data storage
- Comment 1:
- Praised the technical impressiveness of our specific submodule and its broad applicability to many projects
- Suggested removing unnecessary data displays like the radar graph, as users may not understand its purpose or relevance
- Comment 2:
- Enjoyed both the presentation and demonstration overall
- As a teacher, expressed excitement about the grading feature and CSV export functionality for administrators
- Recommended aligning the CSV export format directly with existing gradebook formats by collaborating with teachers to meet real classroom needs
Future Directions
Improvments on Current Project
- Reducing Information-Heavy frontends for user and giving neccesties not wants
- Incorporating the CSV export feature for teachers to increase usabilty
- Grading each technical module, not off completition, but off time spend on module, to promote accountabilty
CSA Learning
- I want to learn to skills to further full-stack skills
- Learning and practicing the remaining topics required for AP exam
- How to communicate effectivley between teams, not within
Analytics
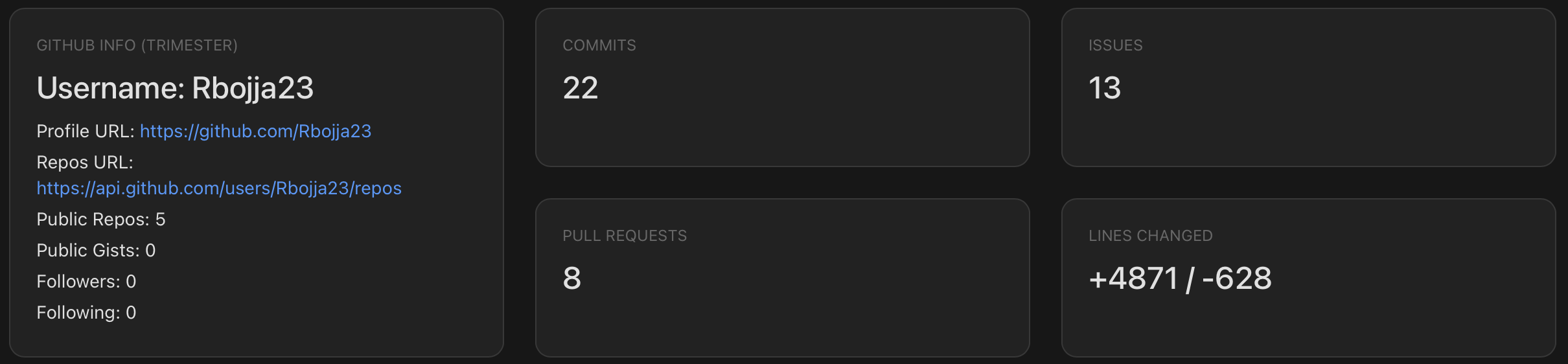
MCQ Analytics, Corrections, and Future Directions
Score: 26/42

Weaknesses:
- Casting and Range of Variables
- Method Signatures
- Math Class
- Comparing Boolean Expressions
- Using Text Files
- Array List Method and Traversals
- Array List Algorithims
- 2D Array Creation and Access, and Traversals
- Sorting Algorithims
- Recursion
- Recursive Searching and Sorting
Corrections
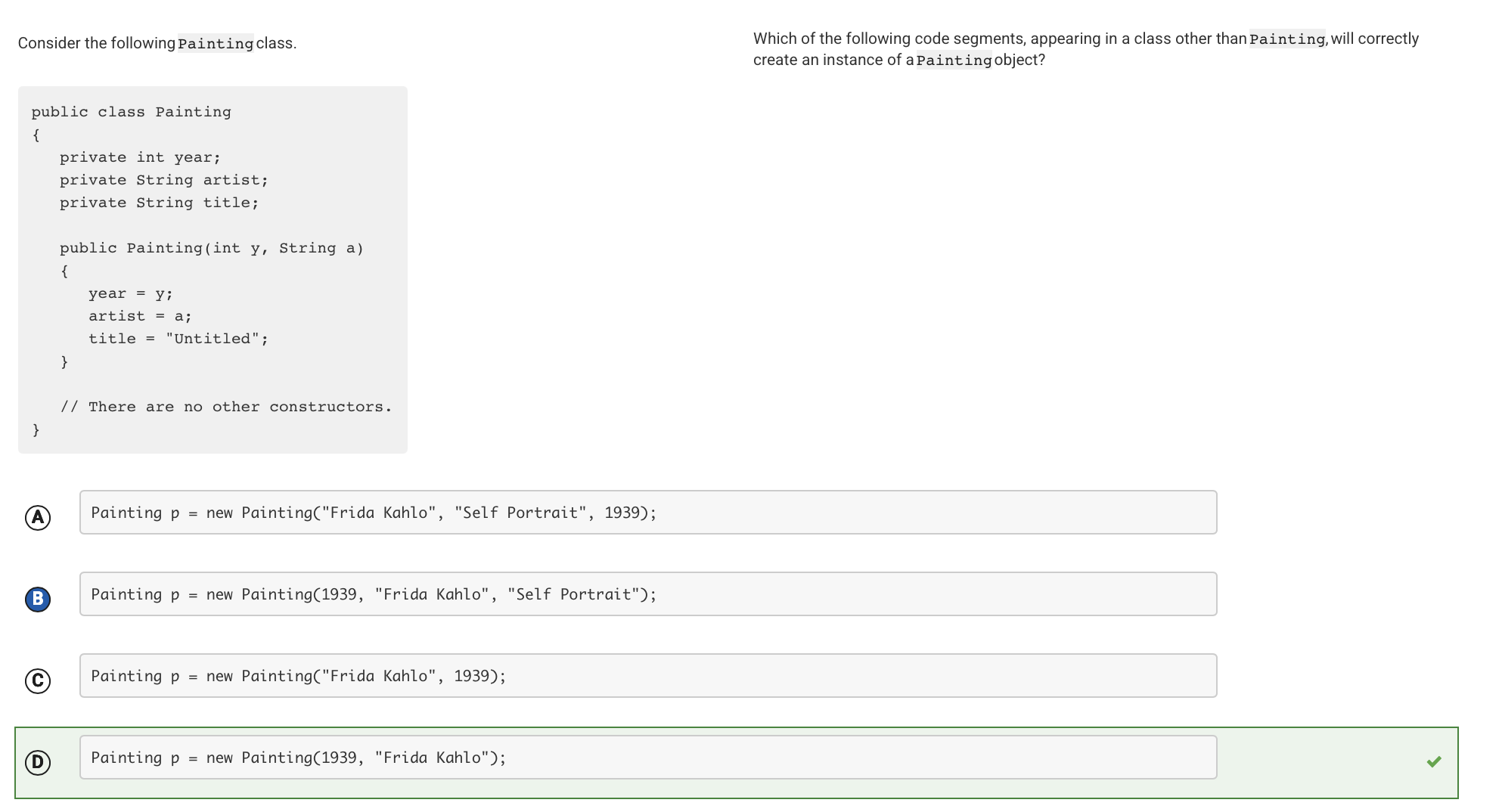
This statement uses the keyword new followed by a call to the Painting constructor. Even though the class has three instance variables, its constructor has only two parameters: an int parameter and a String parameter, in that order. This constructor call has arguments of the appropriate type in the appropriate order.
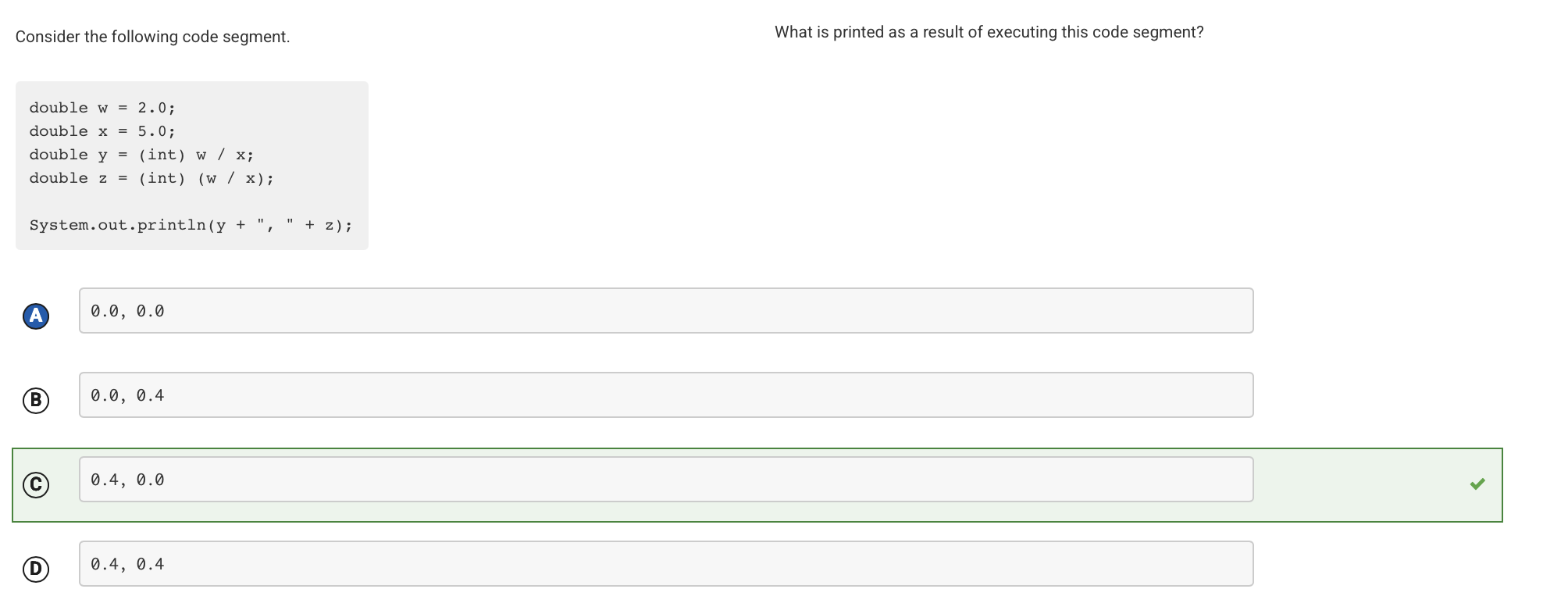
The expression (int) w / x first casts w to the int 2 and then divides the result by the double 5.0. When an int is divided by a double, the int is automatically widened to a double, so the expression is calculated as 2.0 / 5.0, which evaluates to 0.4. The expression (int) (w / x) first divides w by x, which evaluates to 0.4. This result is then cast to an int, which evaluates to 0. This value is then automatically widened to 0.0 when it is assigned to the double variable z.
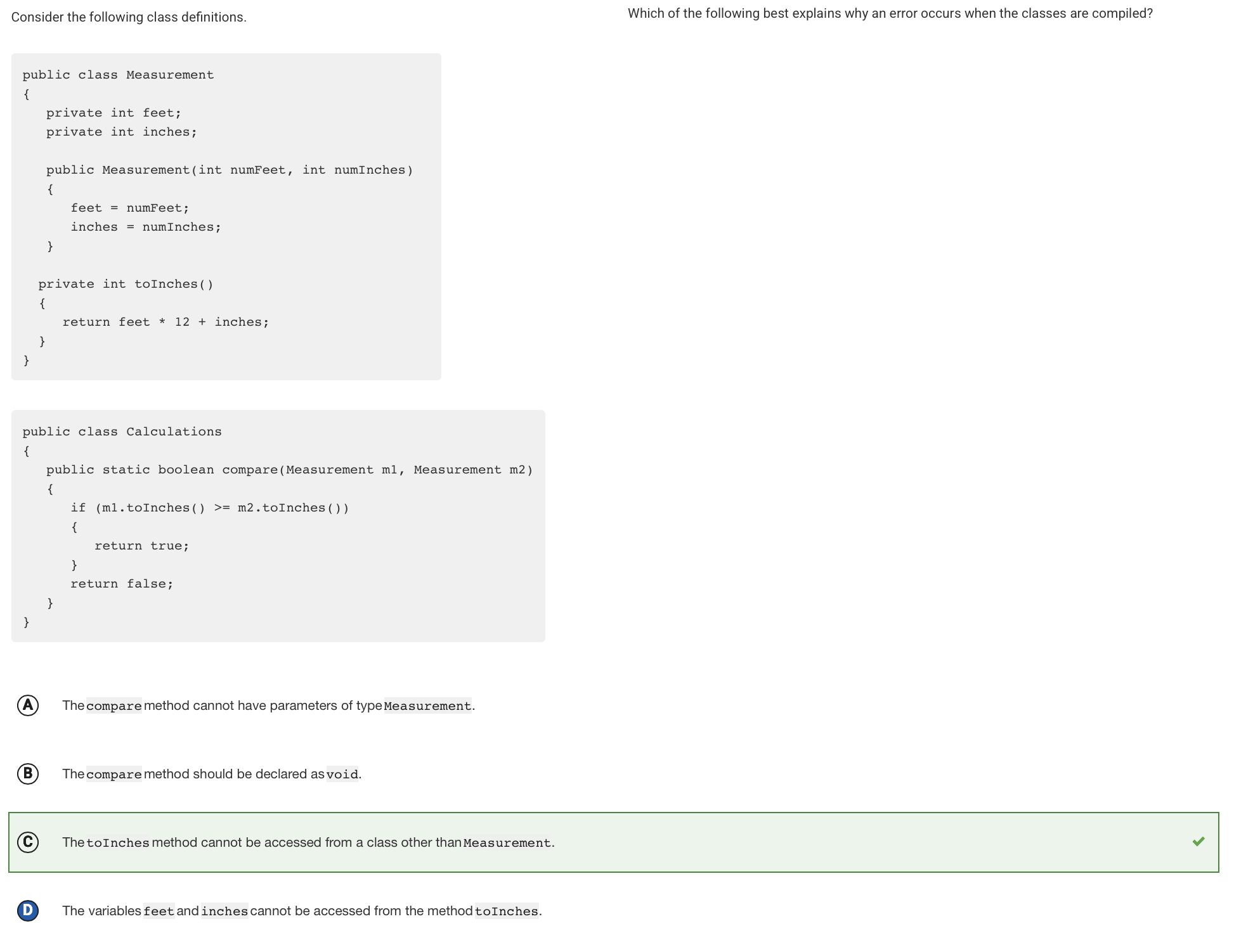
The toInches method is designated as private, so it cannot be accessed from the Calculations class.

| By De Morgan’s law, !(isEven && isPositive) is equivalent to !isEven | !isPositive. The entire expression is equivalent to (!isEven | !isPositive) && isPrime. |

The call Math.random() returns a double greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 1.0. This value is multiplied by 6 to give a double greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 6.0. Casting this to an int gives an integer between 0 and 5, inclusive. Adding 10 gives an integer between 10 and 15, inclusive.
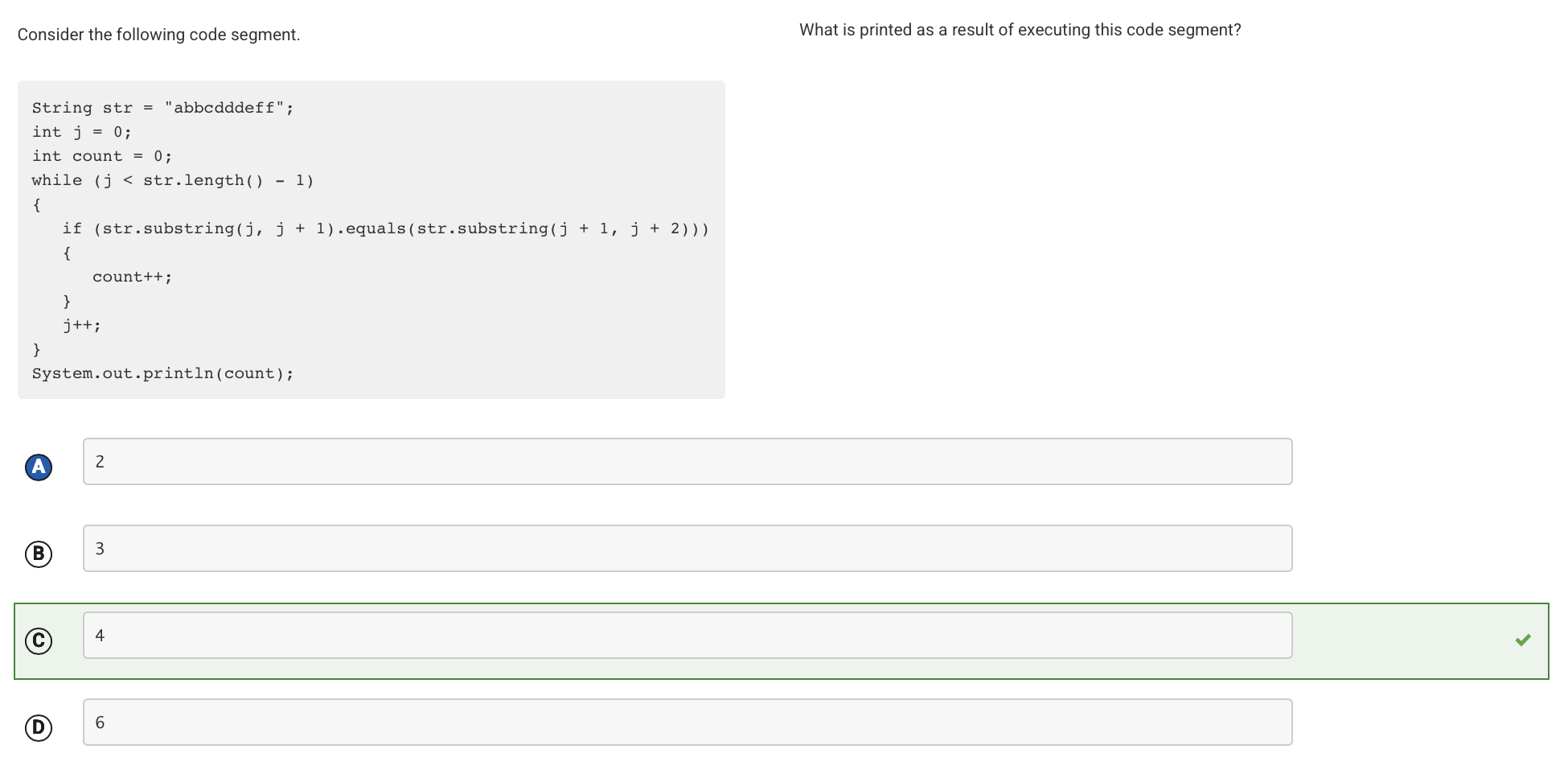
The code segment uses the expression str.substring(j, j + 1).equals(str.substring(j + 1, j + 2)) to compare each character in the string str to the character immediately after it. If they are equal, a counter is incremented. There are 4 places in the string where a character is equal in value to the character immediately after it (one pair of ”b”s, two pairs of ”d”s, and one pair of ”f”s).
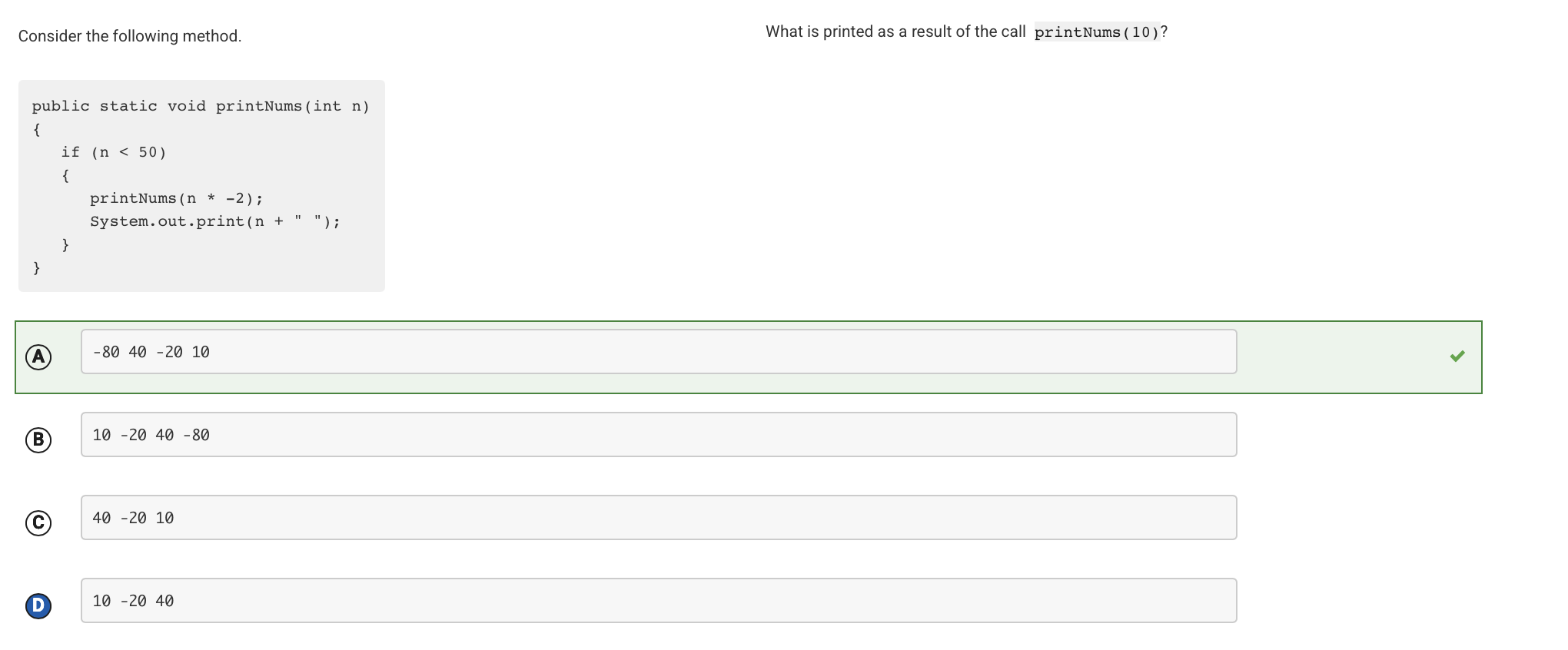
After calling printNums(10), n is less than 50, so printNums(-20) is called. At this point, n is still less than 50, so printNums(40) is called. At this point, n is still less than 50, so printNums(-80) is called. At this point, n is still less than 50, so printNums(160) is called. At this point, n is not less than 50, so there are no more recursive calls. Working backward from the last call, the values of n are printed in the order -80, 40, -20, and 10.

The outer loop header traverses the rows from row 0 to row 1. The inner loop header traverses the columns from column 2 to column 0. The array elements are added to the ArrayList result as they accessed from right-to-left and from top-to-bottom.
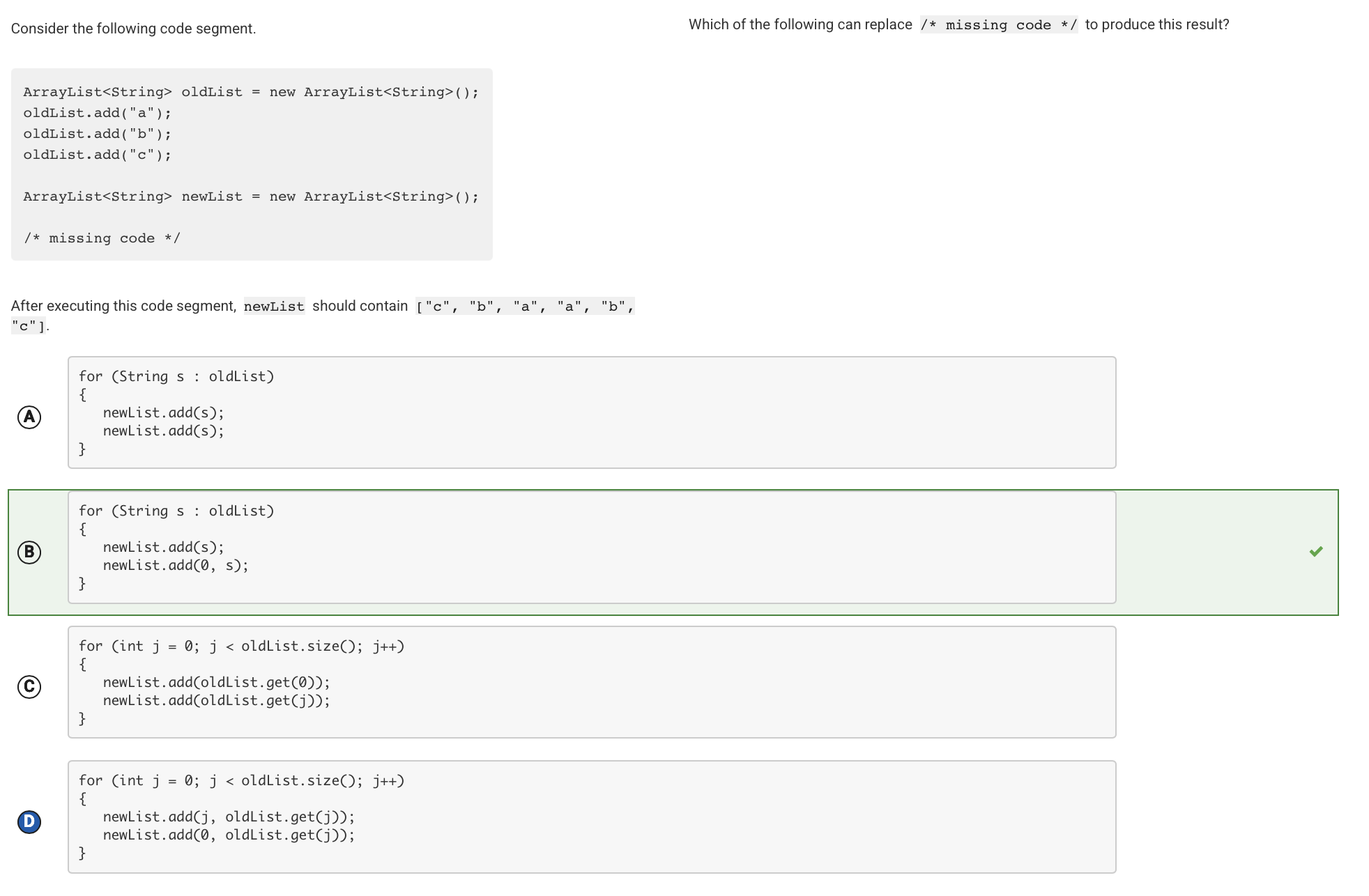
This code segment traverses oldList. For each iteration of the loop, it appends an element from oldList to the end of newList and inserts the same element at the beginning of newList.
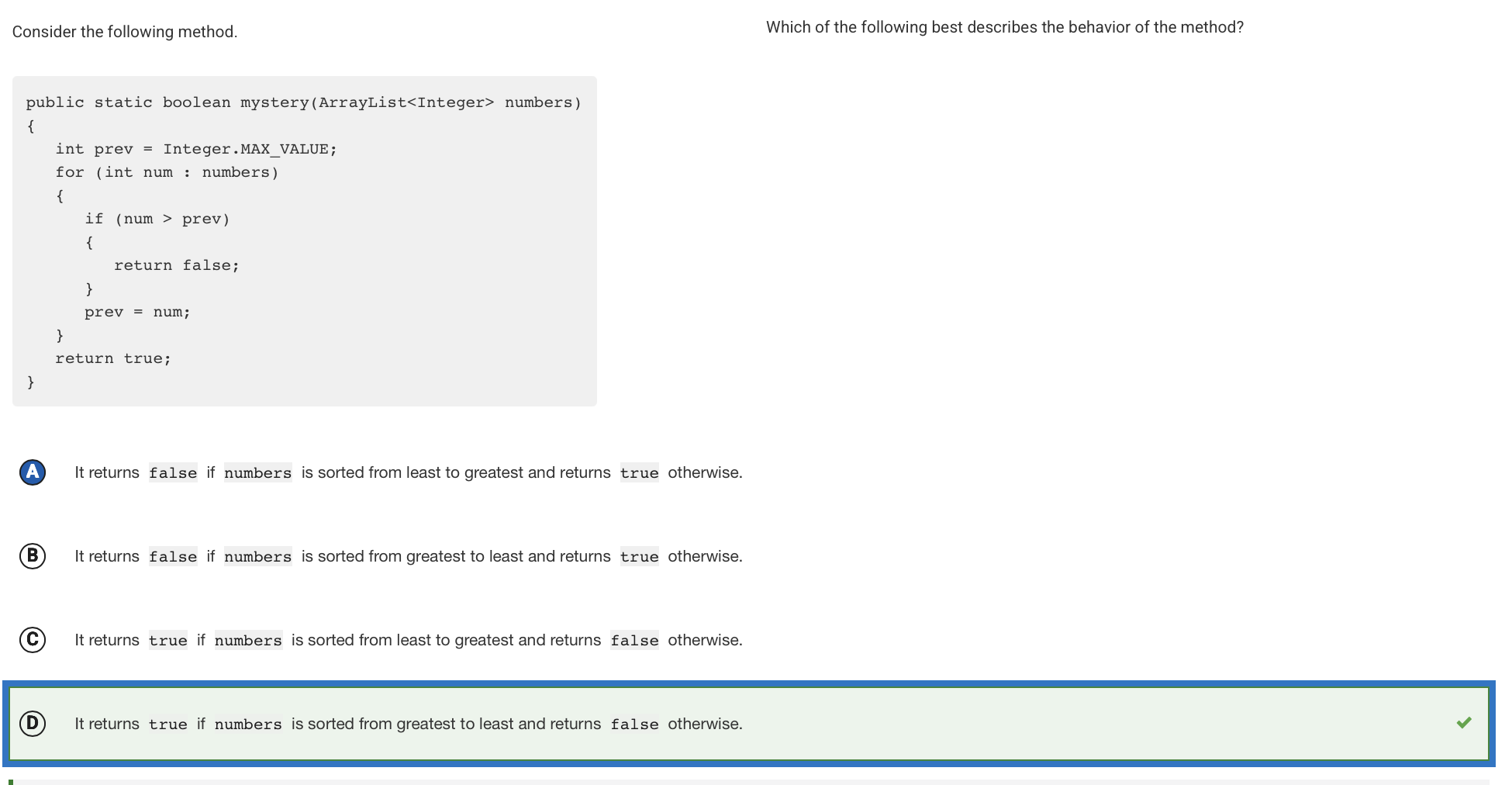
This method compares each ArrayList element to the previous element (except for the first element, which is compared to Integer.MAX_VALUE). If the current element is greater than the previous element, it means the ArrayList is not sorted from greatest to least, and the method immediately returns false. If the code segment traverses the entire ArrayList without finding any elements that are greater than the previous element, it means the ArrayList is sorted from greatest to least and the method returns true.
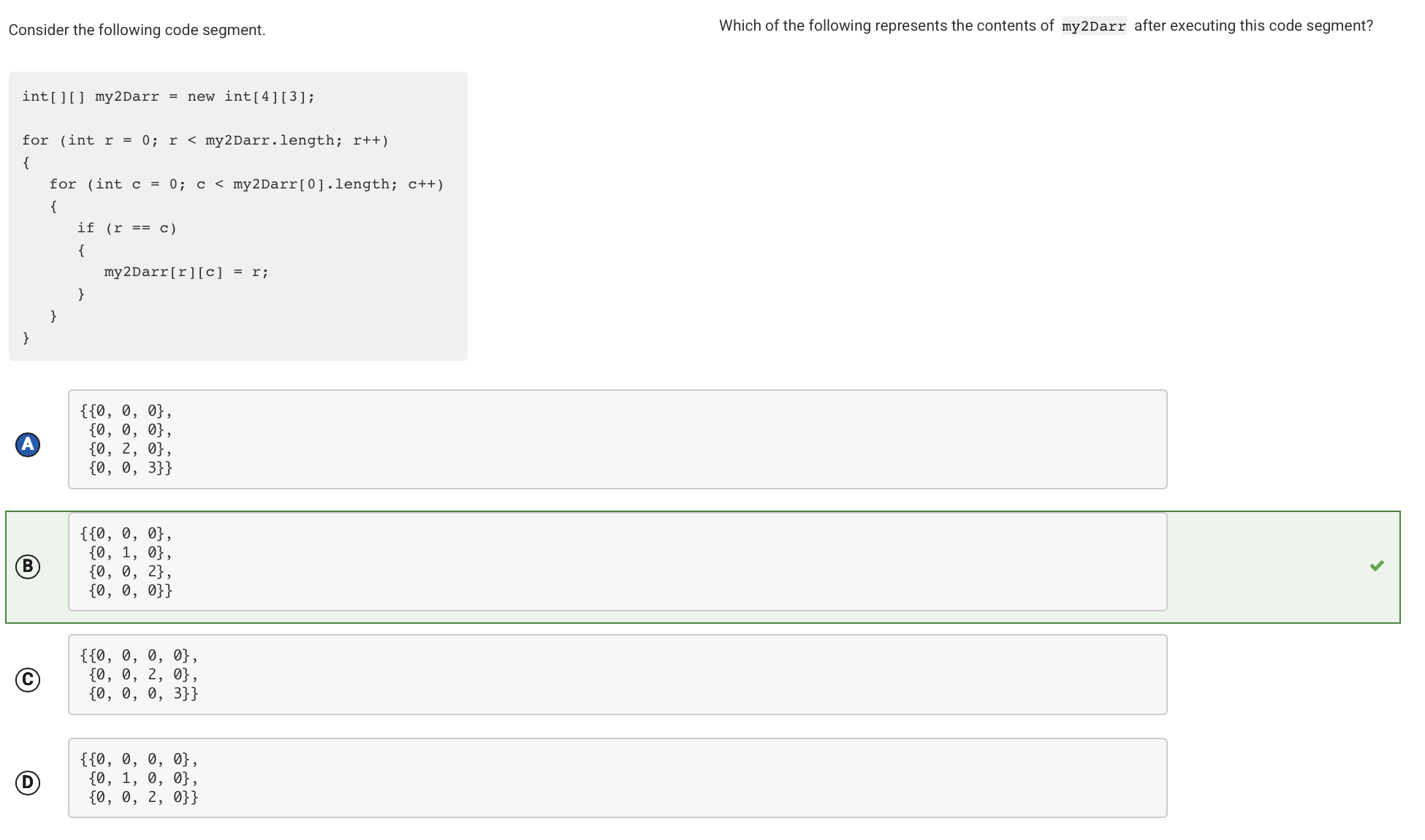
The first line of code creates a new two-dimensional array with 4 rows and 3 columns. By using the keyword new, all elements are initialized to the default value 0. The nested for loops traverse the entire array. When the row index is equal to the column index (which occurs at my2Darr[0][0], my2Darr[1][1], and my2Darr[2][2]), the value of the array element is assigned the value of the row index.
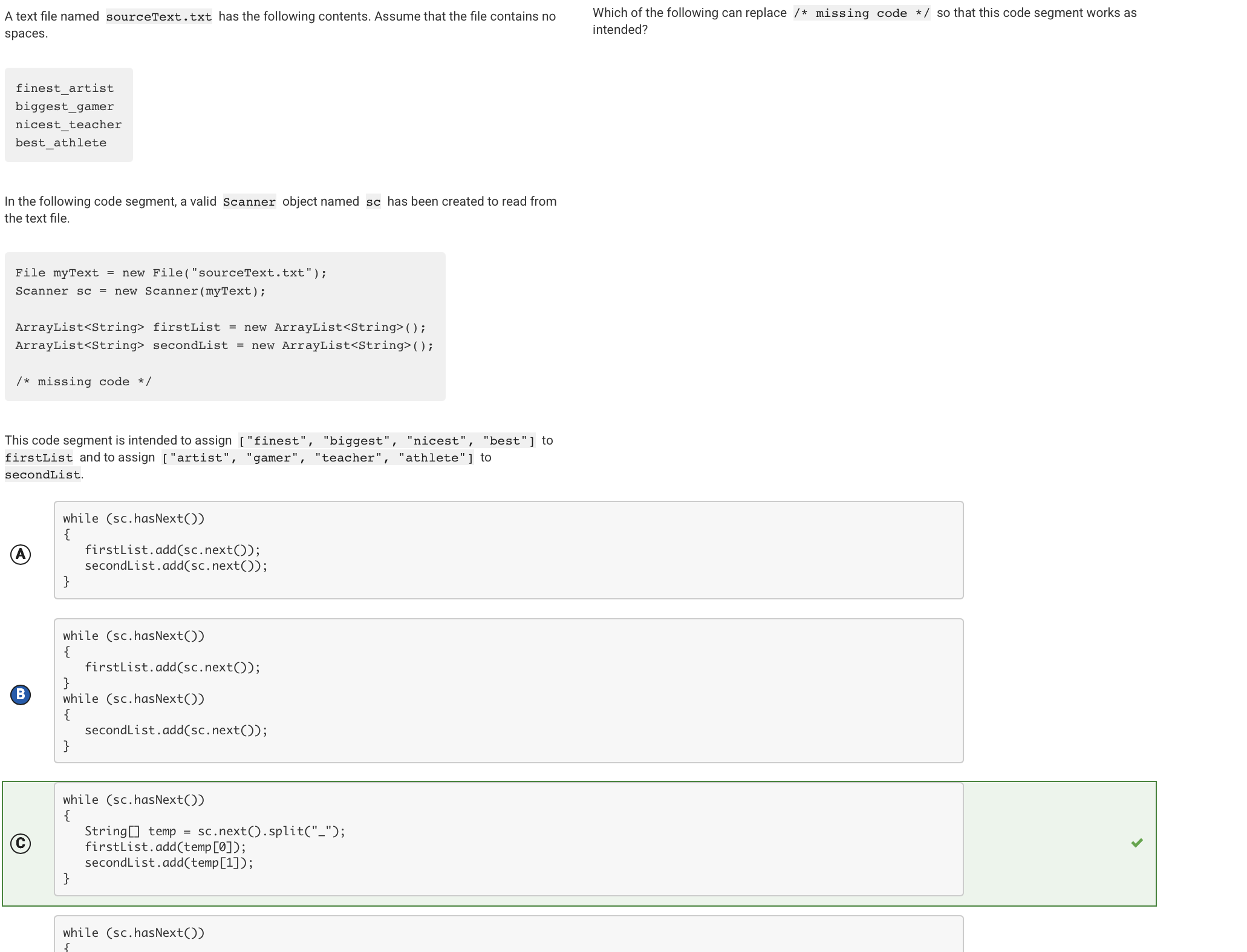
For every string encountered in the file, the code segment will use the split method to place the text before the underscore in temp[0] and the text after the underscore in temp[1]. The value of temp[0] is added to firstList and the value of temp[1] is added to secondList.
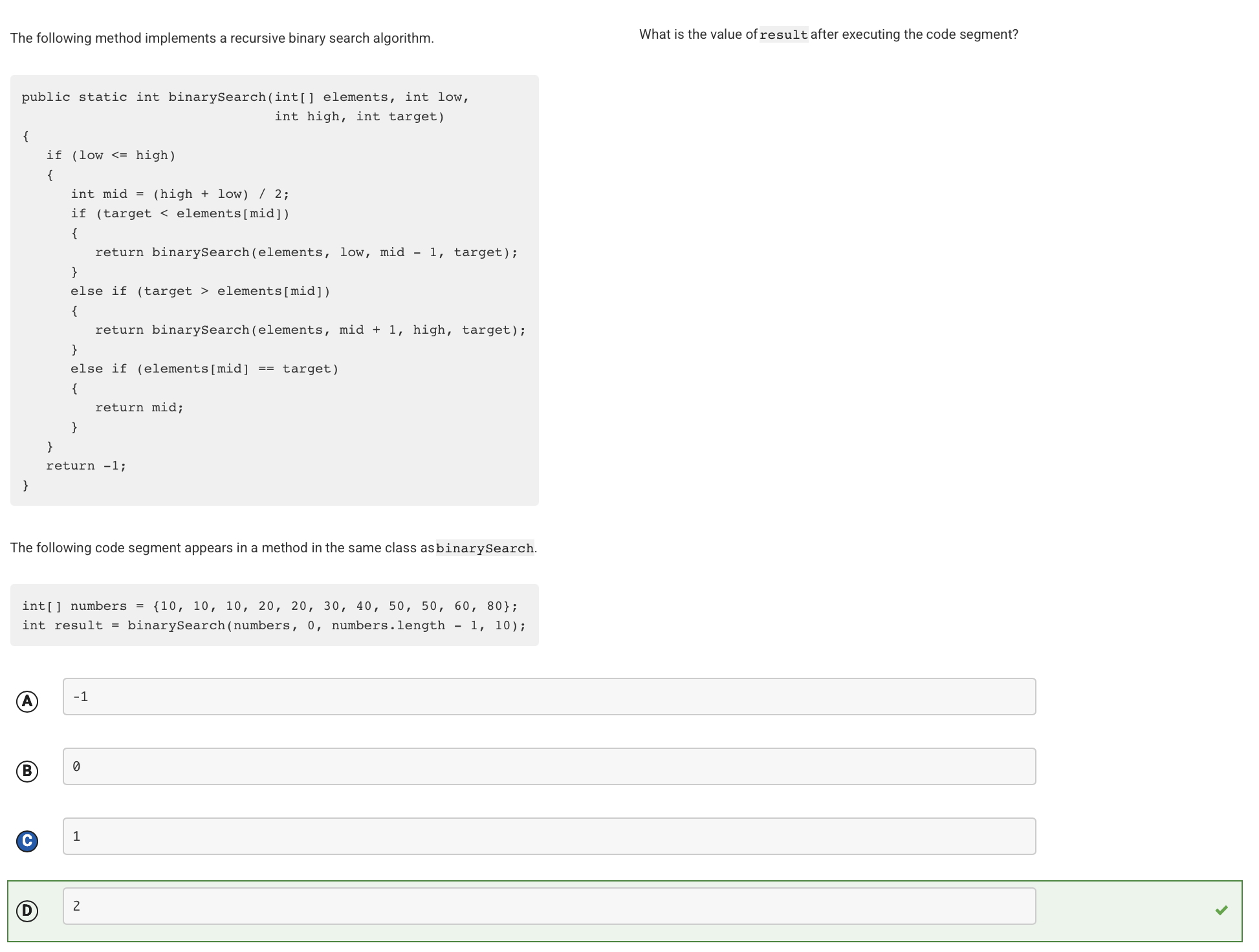
The first time binarySearch is called, low is 0, high is 10, and mid is 5. The value at index 5 is 30, which is greater than target. The next time binarySearch is called, low is 0, high is 4, and mid is 2. The value at index 2 is 10, which is equal to target. The index 2 is returned.
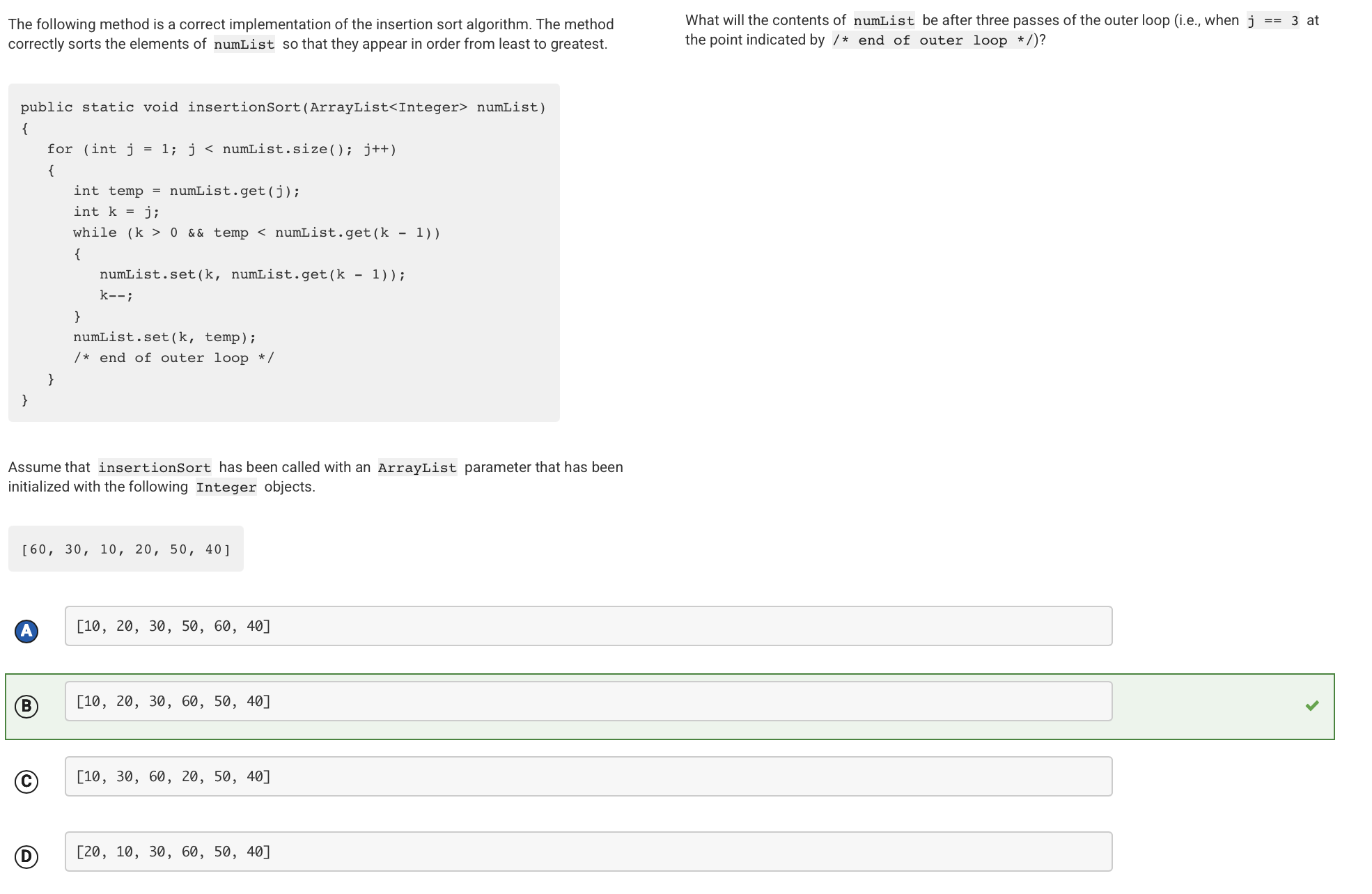
In each iteration of the outer loop, the method moves the element at index j to its proper position in the part of the list from index 0 to index j. After the first iteration of the outer loop, 30 is moved to index 0 so that the contents of numList are [30, 60, 10, 20, 50, 40]. After the second iteration of the outer loop, 10 is moved to index 0 so that the contents of numList are [10, 30, 60, 20, 50, 40]. After the third iteration of the outer loop, 20 is moved to index 1 so that the contents of numList are [10, 20, 30, 60, 50, 40].
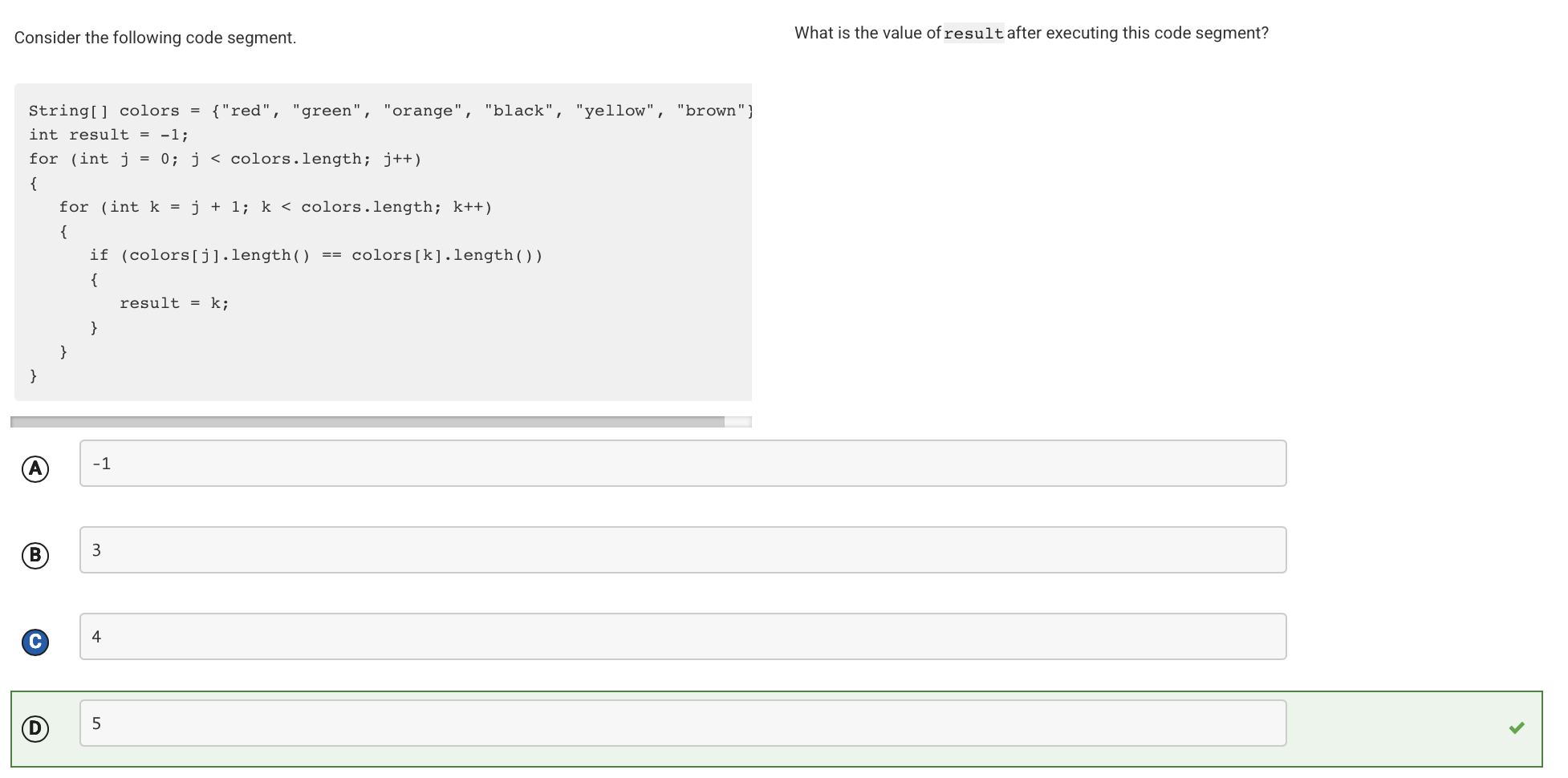
The code segment compares each string element in the array colors with each subsequent string element in the array. If the two strings are the same length, result is assigned k, the index of the string that appears later in the array. As the array is traversed, the last two elements found that have the same length are ”black” and ”brown”. The later of these two elements is ”brown”, whose index is 5.
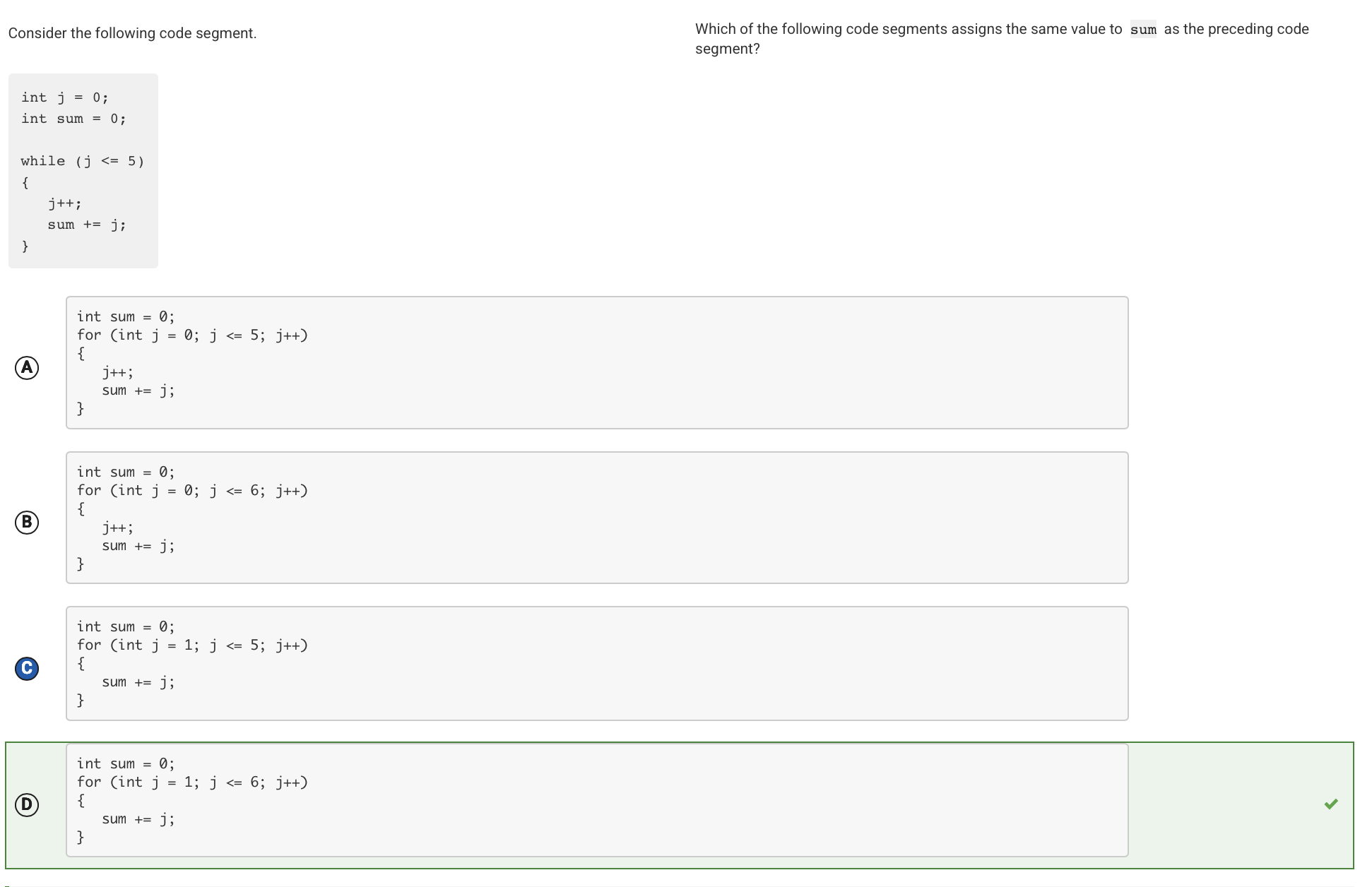
The given while loop calculates the sum of the integers from 1 to 6. It iterates six times (from j = 0 to j = 5), and increments j just before adding it to sum. This for loop also calculates the sum of the integers from 1 to 6. It iterates six times (from j = 1 to j = 6), adding each value to sum.
Future Directions for Improvement
- 2D Arrays
- Practice row-major vs. column-major order traversals
- Focus on understanding when row/column indices are swapped
- Practice initializing arrays and understanding default values
- Recursion
- Trace recursive calls step-by-step on paper
- Understand the call stack and order of execution
- Work on recursive array/ArrayList methods
- ArrayList Algorithms
- Master common operations: add, remove, set, get
- Focus on algorithms that modify lists while traversing
- Understand the difference between adding at specific indices vs. appending
- Sorting Algorithms
- Study selection sort, insertion sort, and merge sort thoroughly
- Trace each algorithm step-by-step through small arrays
- Understand what the array looks like after each pass/iteration
- Type Casting and Data Types
- Memorize casting rules and automatic widening
- Practice expressions with mixed types
- Understand order of operations with casting
- Math Class and Random Numbers
- Memorize the Math.random() range formula: (int)(Math.random() * range) + min
- Practice other Math methods (abs, pow, sqrt)
- Practice: Create 5 random number generators with different ranges
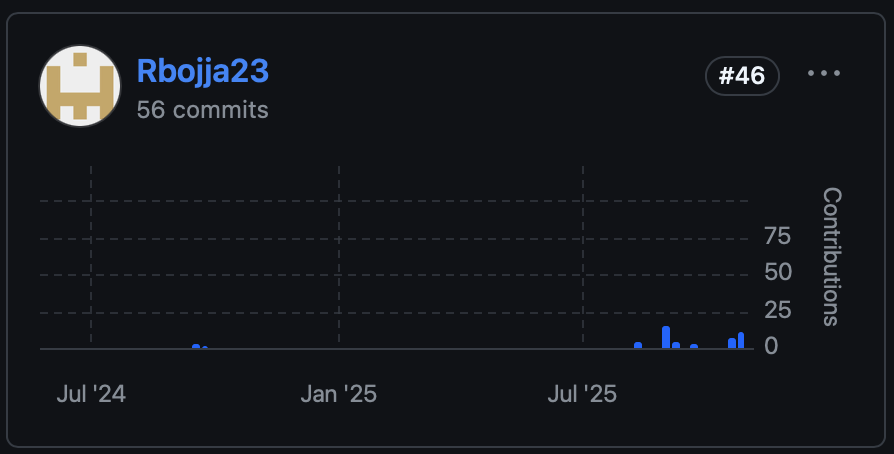
Cool Contribution