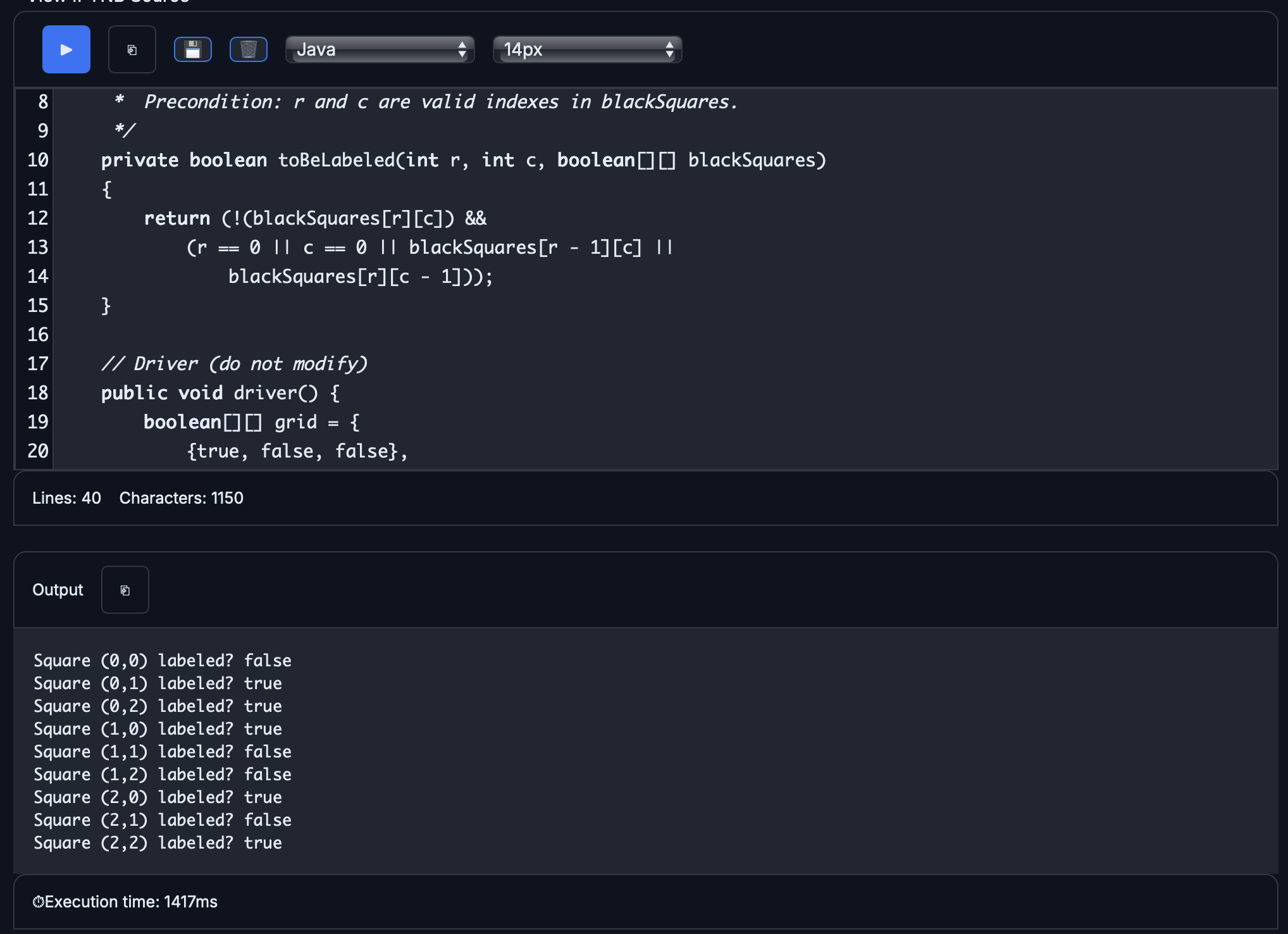
Code:
public class Main {
/** Returns true if the square at row r, column c should be labeled
* with a positive number; false otherwise.
* The square at row r, column c is black if and only if
* blackSquares[r][c] is true.
* Precondition: r and c are valid indexes in blackSquares.
*/
private boolean toBeLabeled(int r, int c, boolean[][] blackSquares)
{
return (!(blackSquares[r][c]) &&
(r == 0 || c == 0 || blackSquares[r - 1][c] ||
blackSquares[r][c - 1]));
}
// Driver (do not modify)
public void driver() {
boolean[][] grid = {
{true, false, false},
{false, false, true},
{false, true, false}
};
for (int r = 0; r < grid.length; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < grid[0].length; c++) {
System.out.println(
"Square (" + r + "," + c + ") labeled? " +
toBeLabeled(r, c, grid)
);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main tester = new Main();
tester.driver();
}
}
Approach
- The method first checks that the square at row r and column c is not black by verifying that blackSquares[r][c] is false.
- It then checks whether the square is located in the first row or first column, since those squares can be labeled if they are not black.
- If the square is not in the first row or column, the method checks whether the square above or the square to the left is black.
- The square should be labeled only when it is white and either on the top/left edge or adjacent to a black square above or to the left.
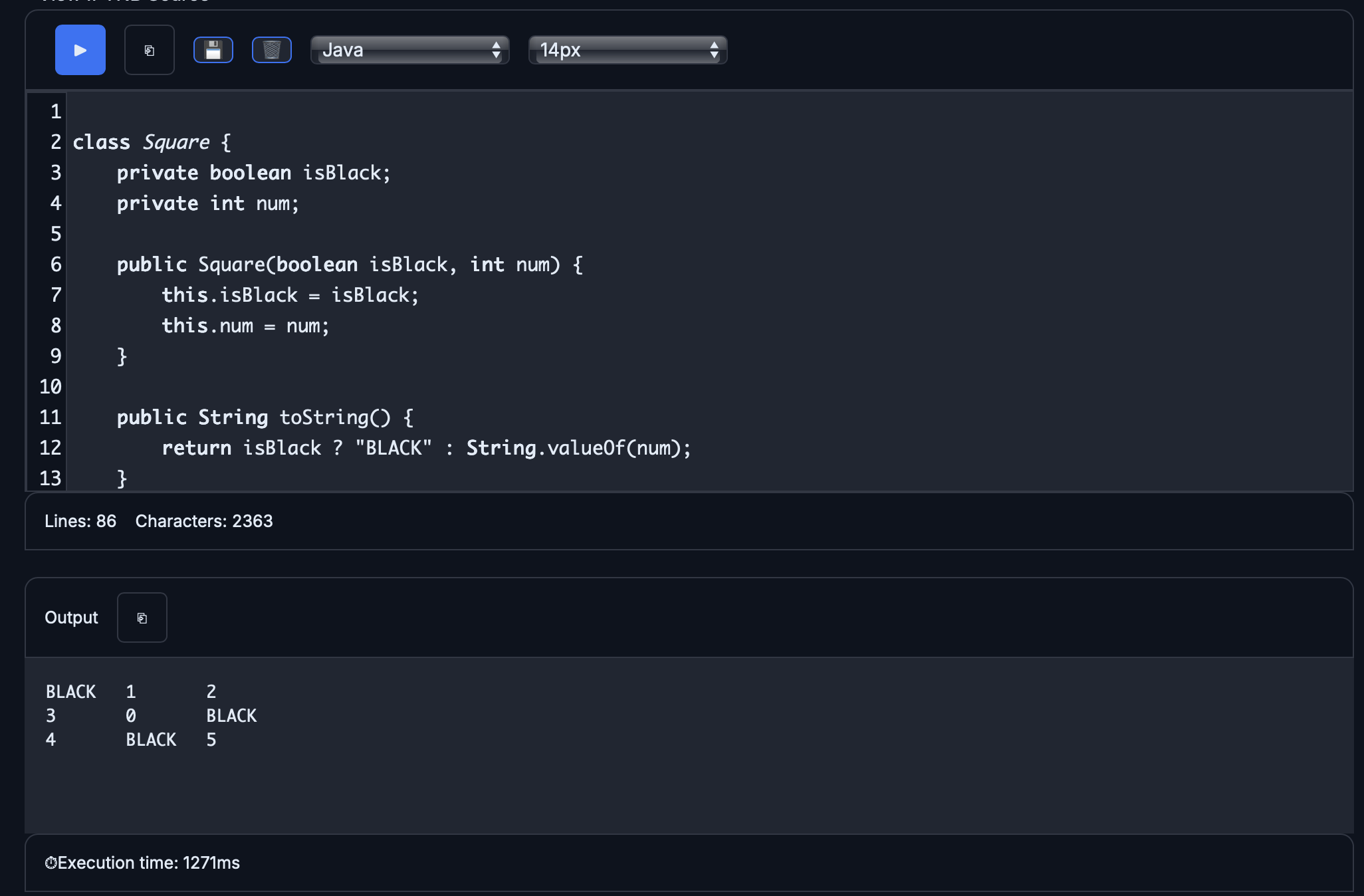
class Square {
private boolean isBlack;
private int num;
public Square(boolean isBlack, int num) {
this.isBlack = isBlack;
this.num = num;
}
public String toString() {
return isBlack ? "BLACK" : String.valueOf(num);
}
}
public class Main {
private Square[][] puzzle;
// Assume this method works correctly (given in Part a)
private boolean toBeLabeled(int r, int c, boolean[][] blackSquares)
{
return (!(blackSquares[r][c]) &&
(r == 0 || c == 0 || blackSquares[r - 1][c] ||
blackSquares[r][c - 1]));
}
/** Constructs a crossword puzzle grid.
* Precondition: There is at least one row in blackSquares.
* Postcondition:
* - The crossword puzzle grid has the same dimensions as blackSquares.
* - The Square object at row r, column c is black if and only if
* blackSquares[r][c] is true.
* - The squares in the puzzle are labeled according to the crossword labeling rule.
*/
public Main(boolean[][] blackSquares)
{
puzzle = new Square[blackSquares.length][blackSquares[0].length];
int num = 1;
for (int r = 0; r < blackSquares.length; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < blackSquares[0].length; c++)
{
if (blackSquares[r][c])
{
puzzle[r][c] = new Square(true, 0);
}
else
{
if (toBeLabeled(r, c, blackSquares))
{
puzzle[r][c] = new Square(false, num);
num++;
}
else
{
puzzle[r][c] = new Square(false, 0);
}
}
}
}
}
// Driver (do not modify)
public void driver() {
for (Square[] row : puzzle) {
for (Square s : row) {
System.out.print(s + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean[][] grid = {
{true, false, false},
{false, false, true},
{false, true, false}
};
Main crossword = new Main(grid);
crossword.driver();
}
}
Approach
- The constructor creates a puzzle grid with the same number of rows and columns as the given blackSquares array.
- It uses a counter num starting at 1 to assign crossword labels to appropriate squares.
- For each position (r, c), if blackSquares[r][c] is true, it creates a black Square and places it in the puzzle.
- If the square is not black, it calls toBeLabeled(r, c, blackSquares) to decide whether that square should receive a label.
- When a square should be labeled, it stores the current label number and increments it; otherwise, it creates a white square with label 0.